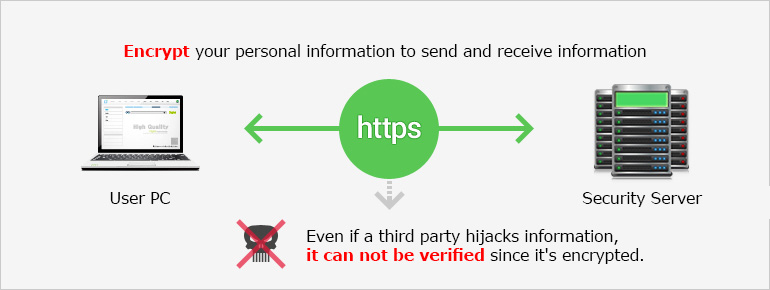
Individuals accessing a website without a security server from a PC on a public network are at a significant risk of having their personal information exposed. Any personal information (e.g. ID, password, e-mail address, resident registration number, address, phone number, etc.) sent in this environment can be easily obtained by any ill-intentioned individuals using a sniffing tool. To prevent this, a security server can be set up in order to safely transmit messages using the standard encryption technique conforming to the international security standards. This is why a security server is absolutely necessary for personal information protection..
Prevention of Forgery and Tampering (Assurance of Integrity)A security server guarantees the integrity of the transmitted messages. It prevents any forgery or tampering of the messages sent from the web browser of the user to the web server as a way to ensure reliable message transmission.
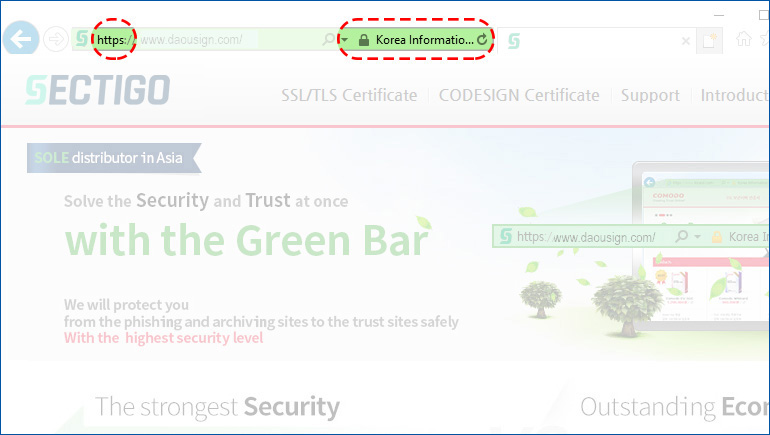
Prevention of Fake and Fraudulent Websites (Prevention of Phishing)It is difficult to attempt phishing on a website with a security server. You can distinguish a fake and fraudulent website that may bear resemblances to the actual website by checking whether there is an image of a lock on the webpage or whether there is an encrypted call (https://) or an encryption module loading page appears when you enter your personal information.
Improved Confidence in the CompanyEnterprises that set up a security server for their websites can bolster their image as a company that safely protects and manages the personal information of their customers. The security server certification mark provided by the KICA is an indication that a security server has been set up for the website and informs visitors of the security measures that have been taken to protect their personal information. Clicking on the certification mark presents related security information such as the serial number of the certificate, the name of the issuer of the certificate and so on. Also, the Green Bar function, which changes the address bar to a green color, instantly tells visitors that they can trust the website to be safe and secure. This is why the vast majority of institutions and organizations that handle personal information such as financial institutions and public agencies have applied this to their websites.
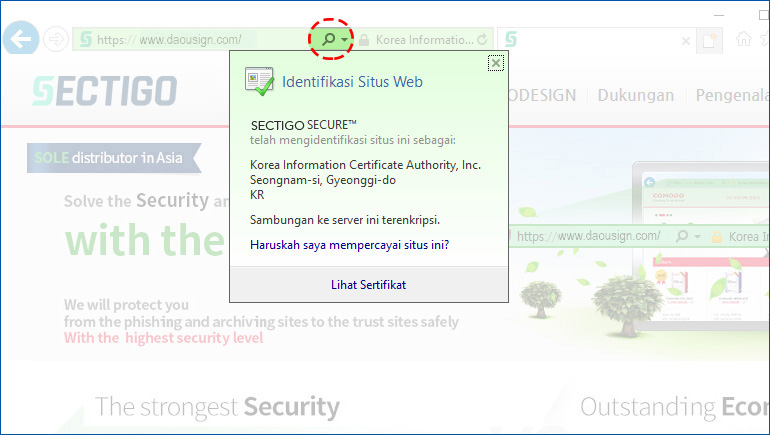
Security servers can largely be divided into two types based on whether the SSL technology or an application program has been applied. If it is unnecessary to install an additional security program for the web server and the web browser, an SSL security server can be set up by installing and applying an SSL certificate on the web server that is currently in use. An SSL security server can be identified by the mark in the image of a lock on the side of the address bar and on the status bar at the bottom of the browser when accessing the webpage requiring secure communication. However, depending on the website configuration method, the lock-shaped mark may not be visible to the visitors. You can click on the lock to check the website certificate and its validity period among other information.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Country | Country Code |
| State / Province | Full Name of the City/Province |
| Locality | Name of the City (-si)/County (-gun)/District (-gu) |
| Organization | Company Name |
| Organization Unit | Department Name (enter the desired name) |
| Common Name | Example of Preparing CSR ?? Full Domain |


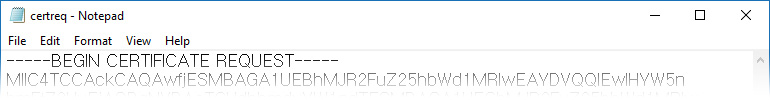
The personal key, which pairs with the certificate that will be issued, is sensitive information that must be safely stored. In case of leakage, the SSL secure communication will inevitably break down. This is why the personal key and the corresponding password must be safely stored and managed by the officer in charge of certificate management. In case of loss, recovery is not possible and a new certificate must be issued by going though the same procedure as the issuance of the original certificate.
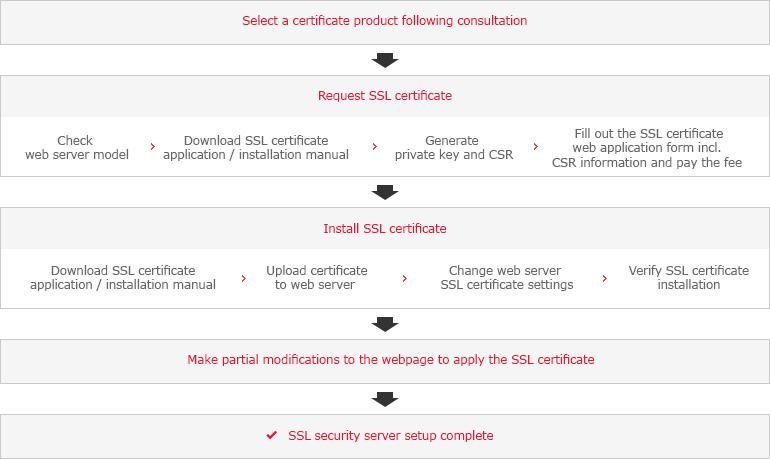
An SSL certificate is installed on the web server. The installation procedure is as follows:
The SSL certificate installation procedure varies according to the type of web server in use. For detailed information on how to install the SSL certificate for each type of web server, click on the following link.
View Certificate Installation Manual for Different Web Servers
Precautions for SSL Certificate InstallationAn SSL certificate is installed on the web server and has nothing to do with WAS in relation to the certificate apply and installation procedures.
Generally, SSL port is not shared when the certificate is applied. Thus, the port must be set for each domain when applying the certificate.
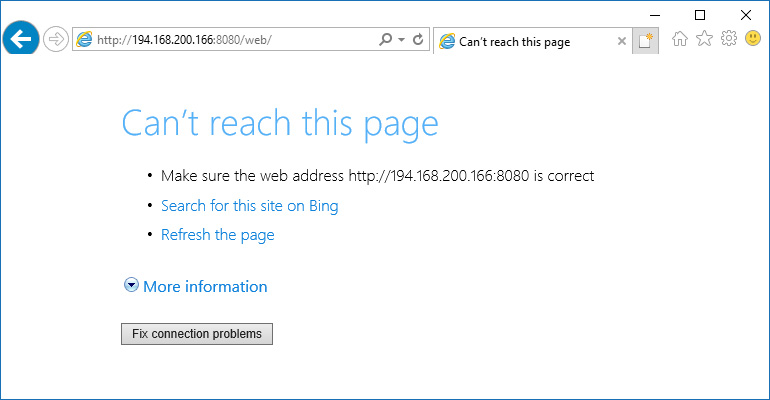
If you are prompted with the error message, “This page cannot be opened,” as shown in the following figure even after reloading the server properly following the installation and application of the web server SSL certificate, it is often the case that Port 443 or the port specified as the HTTPS port is closed on the firewall or the web application firewall. If it is a firewall, then open the port in question, and if it is a web application firewall, open the port in question and install the SSL certificate and personal key in the corresponding domain setting in case the scanning function for HTTPS (SSL encrypted communication) is active.
Occasionally, there is a need to install a route and chain certificate depending on the type of web application firewall that is being used. For more details on how to handle such situation, please contact the person in charge of the web application firewall.
Even after the SSL certificate has been installed on the web server, the security server setup process is not entirely finished. For proper operation of the security server, there is a need to apply the SSL certificate to the webpage so that SSL encrypted communication (HTTPS protocol) is made possible for the web server using the SSL certificate.
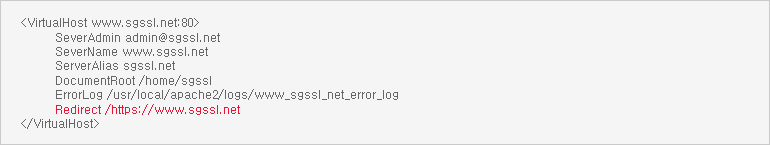
In order to apply the SSL certificate, change “http://” to “https://” as shown in the following figure.

There are two ways to apply the SSL certificate to a website: encrypting all of the webpages or encrypting only certain webpage of the site. Encrypting all of the webpages requires a simple editing of the source, but because it encrypts pages that do not necessarily have to be encrypted, it exerts a larger load on the server compared to partial encryption.
Encrypting only certain webpages of the site is more complicated in terms of source editing compared to total encryption, but this method can prevent any unnecessary load on the server.
The method of encrypting the entire website involves the use of a redirection function. The redirection function forcibly redirects the visitor to a different address or page as a means to prevent any inconveniences to the visitors and to start encrypted communication right away.
The following items are examples of implementing the HTTPS redirection function using an HTML tag, JavaScript, web server setting, etc.


Partial encryption of the website involves choosing between encrypted transmission or unencrypted transmission when moving from one webpage to another.
The following is an example of applying SSL encrypted communication to the log-in page. When the ID and password, which are sensitive information of the user, are transmitted via the network, the data are encrypted to ensure safe and secure transmission of the user’s personal information.
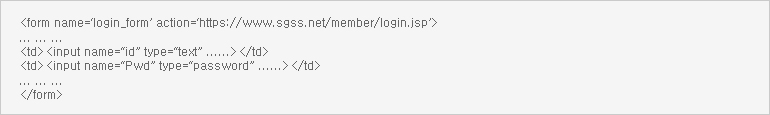
After the SSL certificate is applied to a webpage, a warning window, shown below, may open.
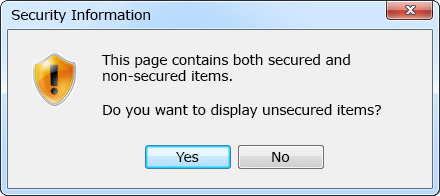
This occurs when there is an item that has not been secured with HTTPS within the webpage called using https://. This is a normal function of web browsers to inform the user that the webpage is partially unencrypted.
In order to prevent this warning window from appearing, find all of the parts that are not secured with HTTPS in the webpage source to be called as https:// and edit them so that they can be called as https://.
6. The term “personal information” means the information pertaining to an individual who is alive and refers to information in the form of a code, letters, voice, sound, image, etc. with which a specific individual can be identified by his or her name, resident registration number, etc. (incl. information with which a specific individual cannot be identified when used alone but can be identified when used in combination with other information)
Article 28 (Protective Measures for Personal Information)
① Information and communications service providers, etc. shall, when handling personal information, take the following technical and administrative measures in accordance with the guidelines prescribed by Presidential Decree to prevent any loss, theft, leakage or tampering of or damage to the personal information:
4. Security measures using encryption technology, etc. for safe storage and transmission of personal information
Article 76 (Administrative Fines)
① Any individuals falling under any of the following and individuals committing any of the acts specified under subparagraphs 7 through 11 shall be punishable by an administrative fine not exceeding 30 million won <Amended on March 29, 2011, Feb. 17, 2012>
3. An individual who fails to take the technical and administrative measures pursuant to Article 28 (1) (incl. cases applicable mutatis mutandis according to Article 67)
④ Pursuant to Article 28 (1) 4 of the Act, information and communications service providers, etc. shall take the following security measures to ensure the safe storage and transmission of personal information:
3. Measures such as setting up a security server in case of sending and receiving the personal information and authentication information of users via an information and communications networks [Wholly Amended, Jan. 28, 2009]
① Technical measures necessary for ensuring the security of personal information pursuant to Article 28 (1) and Article 67 (1) are as follows: 5. Any other technical protection measures necessary for ensuring the security of personal information;
Standards for Technical and Administrative Protection Measures for Personal Information [Korea Communications Commission Notice No. 2012-50] Article 6 (Encryption of Personal Information)
① Information and communications service providers, etc. shall, when sending and receiving the personal information and authentication information of users, encrypt the information by setting up a safe security server, etc. The security server shall have one of the following functions:
1. The function of encrypting the transmitted information, with the installation of Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate on the web server, for sending and receiving information;
2. The function of encrypting the transmitted information, with the installation of an encryption application program on the web server, for sending and receiving information
[Note] Types of Personal Information
| Type | Example of Personal Information |
|---|---|
| Personal Information Details | Name, resident registration number, address, domicile of origin, contact information such as phone number, date of birth, place of birth, e-mail address, family relations and information on the family composition, etc. |
| Physical Information | (Physical Information) Face, fingerprints, irises, voice, genetic information, height, weight, etc. (Medical/Health Information) Health status, medical records, physical disabilities, disability grade, medical history, etc. |
| Information on the Mind (i.e. Intellect and Ideas) | (Information on Preferences/Propensities) Records of book/video loans, magazine subscriptions, goods purchased, online searches, etc. (Inner Secrets, etc.) Views, creeds, religion, values, party/labor union membership and activity, etc. |
| Information on Properties & Assets | (Financial Information) Income, credit card number, bank account number, movable assets and real estate properties, savings, etc. (Credit Information) Credit rating, loans or securities established, credit card statement, etc. |
| Social Information | (Education Information) Educational background, grades, attendance record, qualification certificates, rewards/penalizations, student records, etc. (Legal Information) Criminal record, trial records, payment of fines/penalties, etc. (Labor Information) Profession, employer, place of work, work experience, rewards/penalizations, job performance evaluation records, etc. (Military Service Information) Fulfillment of compulsory military service (Y/N), service number, rank, unit, etc. |
| Other | Phone call history, website access history, e-mails or text messages, location information determined by GPS, etc. |
Please enter your road address and building number, or dong/ri and lot number.
(E.g.: Yeonji-dong 219-2, Sejong-daero 110)
| Please enter your road address and building number, or dong/ri and lot number. |